The Mediterranean diet is a healthy way to eat that focuses on food as the primary source of nutrients rather than calorie-dense processed foods. It encourages eating plant-based foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, beans, nuts, olive oil, fish, and poultry while limiting red meat and sweets.
The diet is rich in plant-based foods and healthy fats, such as olive oil. The Mediterranean diet also encourages eating fish two times per week and choosing lean cuts of meat over fatty ones (especially red meat).
The Mediterranean diet has been shown to improve overall health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, reduce saturated fat and promote weight loss. This article provides an overview of the critical components of the diet and how to get started.
- What is the Mediterranean Diet
- What Can You Eat on the Mediterranean Diet
- Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
- Reduce Heart Disease Risk Factors
- Improve Triglycerides and HDL Cholesterol
- May Lead to Weight Loss and Help Fight Obesity
- Help Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
- May Aid Blood Sugar Control in People With Diabetes
- It contains Beneficial Compounds, Including Fiber, Antioxidants, and Omega-3s.
- May Help Fight Inflammation
- What Foods to Eat on a Mediterranean Diet?
- The Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan: A 7-Day Sample
- The Mediterranean diet focuses on lifestyle, not restriction or depriving yourself of your favorite foods.
- Alternatives to the Mediterranean Diet
- Conclusion
What is the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is a popular way of eating based on the traditional foods and styles of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea.
There isn’t just one Mediterranean diet; many different versions depending on the country. The common thread emphasizes fresh, healthy ingredients like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and olive oil.
The diet has many health benefits, including a lower risk of heart disease and stroke, an improved immune system, and a reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
If you’re interested in trying out the Mediterranean diet, plenty of resources are available to help you get started. For beginners, we recommend checking out our article on the basics of the Mediterranean diet.
What Can You Eat on the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is one of the world’s healthiest diets, and it focuses on eating a lot of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, fish, and nuts.
If you’re thinking about starting the Mediterranean diet, here’s some information about what can and can’t be eaten on this plan.
So what can you eat on the Mediterranean diet? Here are some examples for your shopping list:
Fruits: Fresh fruit should be consumed in season. Some examples include apples, pears, bananas, peaches, and plums. Fresh fruit juices from fresh fruit are also okay to drink as long as they contain less than 10 grams of sugar per 100 milliliters (about 4 ounces).
Vegetables: Vegetables are a key part of the Mediterranean diet. They should be eaten with each meal or as a side dish rather than as the main event because they have more water than most other foods.
The main vegetable in the diet is artichokes (farcies in French). Artichokes can be eaten raw with oil drizzled over them or stuffed with ground beef or lamb seasoned with paprika and lemon juice. Other vegetables include eggplant (aubergine or eggplant), squash (zucchini), asparagus; bell peppers (green); broccoli; Brussels sprouts; cabbage (red or savoy); sweet potato; carrots (orange or purple); cauliflower; cucumbers; eggplant; garlic; mushrooms (white); onions (white) and potatoes (baked, boiled or fried).
Grains: Choose wholegrain bread, pasta, rice, and noodles instead of refined flour, such as white bread or white pasta. It’s also best to choose wholegrain cereal if you’re choosing breakfast cereals.
Eat fish at least twice a week. Fish is an essential part of the diet because it’s high in heart-healthy fatty acids such as omega-3s and antioxidants that fight inflammation in your body.
Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is a great way to improve your health. Here are some of its benefits:
Reduce Heart Disease Risk Factors
The Mediterranean diet may be associated with a reduced risk of heart disease.
The Mediterranean diet has been linked to lower blood pressure, a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
It may also help lower levels of LDL cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol; triglycerides (the substance in the blood that’s high when you’re fat); and inflammation markers like C-reactive protein (CRP).
The benefits are most apparent in people with multiple markers for metabolic syndrome; this is defined as having at least three risk factors for heart attack: diabetes, high blood pressure, high fasting glucose level, and elevated waist circumference (a measure of central obesity).
Improve Triglycerides and HDL Cholesterol
The Mediterranean diet is also suitable for cholesterol levels, as it may improve triglycerides and HDL cholesterol. Triglycerides are fat stored in the body and released into the bloodstream when you eat food.
Too much triglyceride in your blood can cause heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and stroke.
HDL cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein) is considered ‘good’ because it removes excess fatty substances from other cells that could interfere with cell function or damage them if left alone.
HDL Cholesterol: LDL Cholesterol: Triglycerides
May Lead to Weight Loss and Help Fight Obesity
A Mediterranean diet is high in fibre, healthy fats, and fruits and vegetables. This can lead to weight loss because it helps you feel full longer.
When you eat less food than you burn off, your body stores it as fat instead of using it for energy. The Mediterranean diet helps keep your metabolism running at its highest level so that when you eat less, the body will use stored food for energy instead of burning muscle tissue or burning off excess calories through exercise.
Help Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
The Mediterranean diet has been shown to help prevent type 2 diabetes, a severe and potentially deadly disease. One study found that people who followed a Mediterranean-style eating plan had the least risk of developing diabetes compared to those who didn’t.
One study found that following the Mediterranean-style diet could reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes by up to 40 percent!
This makes sense since eating fruits and vegetables has been shown to help lower blood sugar levels (a common sign of diabetes).
May Aid Blood Sugar Control in People With Diabetes
The Mediterranean diet has been shown to improve blood sugar control in people with diabetes. This can be attributed to its high content of fruits and vegetables, which are rich sources of antioxidants and flavonoids that may help reduce inflammation and insulin resistance.
The diet also contains plenty of whole grains, legumes (beans), nuts, and lean meat—all of which have been associated with a lower risk for type 2 diabetes.
An extensive review published in The Journal of the American Medical Association found that following a Mediterranean-style diet could cut your risk by up to 25%.
It contains Beneficial Compounds, Including Fiber, Antioxidants, and Omega-3s.
A Mediterranean diet is rich in fiber, which can help you feel full and keep your digestion running smoothly. Fiber also helps reduce cholesterol levels and promote weight loss.
Antioxidants protect the body from free radicals, which are molecules that damage cells and cause inflammation. They’re found in many fruits, vegetables, nuts, and other foods—but they’re especially abundant in citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits.
Antioxidants have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and cancer prevention; studies show that people who eat a lot of red wine tend to have higher levels of antioxidants than those who don’t drink alcohol much!
Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fatty acids found primarily in oily fish such as salmon or mackerel (not tuna). You need these nutrients if you want healthy brain function by maintaining the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin or dopamine — two chemicals responsible for feelings like happiness or sadness!
May Help Fight Inflammation
Inflammation is a significant cause of chronic diseases, including heart disease and diabetes. It’s also the body’s response to injury or infection.
Inflammation occurs when your immune system mistakenly sees something as foreign (like bacteria) and attacks it as if it were an invader, causing inflammation in the area where that thing was found.
Your body then responds by producing chemicals called cytokines—which can make you feel tired or sick, among other symptoms—to fight off this “invasion.” This process is normal; however, if you suffer from chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis, it may be excessive for your body to produce so much inflammation on its own!
Inflammation helps heal damaged tissue after injury or infection, but too much can lead to problems like osteoarthritis, which causes joint pain throughout our lives. However, research shows us that eating Mediterranean foods regularly may help reduce these effects by reducing oxidative stress caused by high levels of fat intake.
What Foods to Eat on a Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy lifestyle using whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats like olive oil, nuts, seeds, fish, and shellfish.
Fruit is a staple of the Mediterranean diet. It’s full of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Apples, pears, mangoes, melons, and broccoli are all excellent choices.
Starchy vegetables like potatoes and beans are also staples in the Mediterranean diet. But it’s even better to eat them with some fruit.
It’s important to note that this isn’t just about food group choices but also about how much you exercise—a person following this plan should get at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity every week or two days of muscle-strengthening physical activity like weight training three times per week.
The Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan: A 7-Day Sample
To get started, here’s an example of the Mediterranean Diet meal plan for a week. You can use this as a meal template or choose from other options based on what you like.
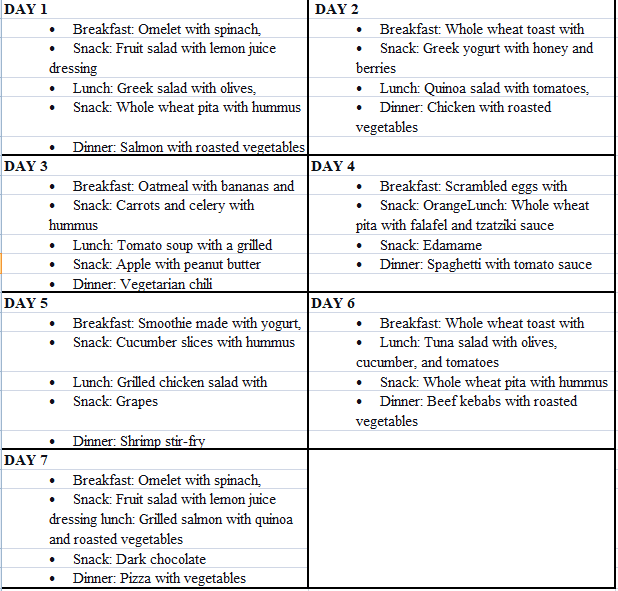
The Mediterranean diet is not a fad but a “diet” at all. The term “Mediterranean diet” refers to the traditional dietary habits of people living in the Mediterranean Basin – i.e., countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea.
The basics of the Mediterranean diet are simple:
1. Eat primarily vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
2. Replace butter with olive oil.
3. Use herbs and spices instead of salt to flavor your food.
4. Limit red meat to a few times per month.
5. Eat fish and seafood at least twice per week.
6. Drink red wine in moderation (optional).
7. Get plenty of exercise.
The Mediterranean diet has improved heart health, cognitive function, and longevity. If you’re looking for a healthy way to eat, the Mediterranean diet is a great place to start!
The Mediterranean diet focuses on lifestyle, not restriction or depriving yourself of your favorite foods.
The Mediterranean diet focuses on a healthy lifestyle, not restriction or depriving yourself of your favorite foods. It would be best to concentrate on eating healthy foods, not foods you are not allowed to eat. The Mediterranean diet has been shown to have many health benefits, including lower rates of heart disease, diabetes, and obesity compared to other diets like Atkins or South Beach Diet.
Alternatives to the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet focuses on a healthy lifestyle, not restriction or depriving yourself of your favorite foods. It would be best to concentrate on eating healthy foods, not foods you are not allowed to eat.
The Mediterranean diet is not the only way to eat healthily. Many other diets can be just as effective in promoting good health.
Here are a few alternatives to the Mediterranean diet:
1. The Paleo Diet: This diet is based on the premise that humans should eat the same foods our prehistoric ancestors ate. The idea is that our bodies are better equipped to handle these foods and that they are more nutritious than the processed foods we typically eat today.
2. The Raw Food Diet: This diet is based on the belief that cooking food destroys its nutrients and enzymes, making it less healthy for us. Proponents of this diet recommend eating raw fruits, vegetables, and meats.
3.E2m Diet: The e2m diet, or “easy to maintain,” is a low-carbohydrate diet with high protein and moderate fat. The e2m diet emphasizes optimal nutrition, focusing on consuming healthy fats, vegetables, and fruits.
4. The Vegan Diet: This diet takes the vegetarian diet one step further and eliminates all animal products from your diet, including dairy and eggs.
5. Keto Diet: The keto diet is one of the most popular diets/lifestyles in recent years. It’s a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet for weight loss and has many health benefits.
Conclusion
The Mediterranean diet is a delicious and healthy way of eating that has been shown to improve overall health and well-being.
This diet is a great place to start if you’re looking for a way to eat healthier. The diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and olive oil — all of which are good for your health.
This diet is easy to follow, so you can start seeing the benefits immediately. Give the Mediterranean diet a try today!
We hope you feel confident about starting your journey towards better health by reading this article!

1 comment
[…] body and better skin. But what exactly does this mean? This new post will explain how a better diet can improve your […]